Charging time for electric cars and what affects the charging speed?
First understand where to charge, what the different charging levels are and have a basic understanding of the difference between AC and DC. Now you can better understand how long it will take to charge your electric car. Levels:
1 (AC) -> 10h-40h
2 (AC) -> 1h-20h
3 (DC) -> 7min-2 h
Charging time for electric cars depends on your vehicle’s battery size, charging capacity, and a number of other situational factors.
To clarify, we have added a summary of the factors below. This overview looks at four average battery sizes and several different charging power outputs.
What affects charging speed?
Electric car battery
The charging time of electric cars depends on the size of the battery. The bigger the battery, the more it will need to be charged. Simple, right? The state of charge of an EV’s battery is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). The vast majority of electric passenger vehicle batteries today can hold anywhere between 25 and 100 kWh when fully charged.
Vehicle charging capacity
The power output that a vehicle accepts varies from vehicle to vehicle and may even vary depending on the car model. The charging capacity plays a big role in its duration. The capacity is for both charging cases, AC and DC. For example, if two vehicles with similar sized batteries are being charged side-by-side at a high-power DC charging station, but one can only accept 50 kW of DC power and the other 250 kW, then the latter will charge too much faster than the first.
Manufacturing charging station charging
Different charging station output plays a big factor in how long it takes to charge an EV. The higher the kW output at a charging station, the faster it will charge (assuming your new vehicle accepts the higher output).
Loaded state
The load you have in your vehicle when you start charging plays an important role. Just like when you put gas in a traditional vehicle. The more space you have to fill in the battery, the more charging time you will need.
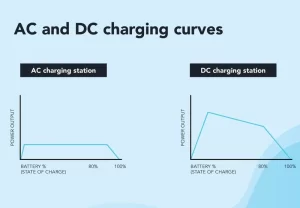
DC charging curve
With AC charging, the power flow in an EV is flat (meaning it will charge at the same rate from 0-100 percent full). With DC charging, the EV’s battery first accepts a faster flow of power and then slowly. It starts to require less power as it starts to fill up. The reason for this is simple. The EV does not want to damage the battery with a power surge. As a result, with a DC or Level 3 charger, the initial phase of charging (up to 80 percent full) goes faster than the last 20 percent.
Kushtet e motit
The charging time of electric cars also depends on the weather. Batteries work more efficiently in warm weather (20-25°C). It will take longer to charge a vehicle in colder or extremely warm weather.